PHOTOBIOMODULATION o NEAR INFRARED LIGHT
It is used in various areas to improve the well-being of the human body; there are numerous scientific articles attesting to its effectiveness.
These scientific studies buy its benefits on the person, and Renovatio is at the cutting edge of technological development.
A recent study also validates its excellent prevention performance for L' ALZEHEIMER.
On which our company is conducting independent research.
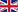
In addition, Renovatio has conducted exclusive research where the result of the treatment on the musculoskeletal system can be verified, with exceptional results.
Scientific Sources
PBM può aumentare la massa muscolare acquisita dopo l'allenamento e ridurre l'infiammazione e lo stress ossidativo.
Effetto della terapia laser a basso livello applicata prima degli esercizi ad alta intensità sul recupero dei muscoli scheletrici negli atleti
La terapia con diodi emettitori di luce può essere utile per ridurre il danno muscolare, il dolore e l'atrofia, nonché per aumentare la massa muscolare, il recupero e le prestazioni atletiche nei programmi di riabilitazione e medicina dello sport.
phototherapy significantly reduced return-to-play in injured university athletes: a pilot study
Photobiomodulation therapy (PBMT) improves performance and accelerates recovery of high-level Rugby players in field test: A randomized, crossover, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study
Protection of skeletal muscles from ischemic injury: low-level laser therapy increases antioxidant activity.
Red (660 nm) and infrared (830 nm) low-level laser therapy in skeletal muscle fatigue.
Effects of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on the nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB signaling pathway in traumatized muscle.
Role of low-level laser therapy on the cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction: A systematic review of experimental studies.
Effect of low-level phototherapy on delayed onset muscle soreness: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Low-level laser (light) therapy increases mitochondrial membrane potential and ATP synthesis in C2C12 myotubes with a peak response at 3-6 h.
Photobiomodulation of the microbiome: implications for metabolic and inflammatory diseases.
Illumination with 630 nm Red Light Reduces Oxidative Stress and Restores Memory by Photo-Activating Catalase and Formaldehyde Dehydrogenase in SAMP8 Mice.

PMB - LLLT
NEAR INFRARED LIGHT
Pioneer in the discovery of phototherapy and its applications was Nobel Prize winner Niels Ryberg Finsen.
In the early 1990s, however, red light was used by scientists to help plants grow in space.
Scientists discovered that the intense light from red light-emitting diodes (LEDs) helped to promote growth and photosynthesis of plant cells.
Red light was then studied for its potential application in medicine, more specifically to find out whether red light could increase energy within human cells; with surprising results.
The photoabsorption of radiation by enzymes, also we already know it.
NO (Nitric Oxide)
ROS (Reactive Oxygen Series) → PKD (gene) → IkB (Inhibitor κB) + NF-κB (nuclear factor κB) → NF-κB (nuclear factor κB stimulates gene transcription)
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) → cAMP (catabolite activator protein) → Jun/Fos (oncogenic transcription factors)
→ AP-1 (activator protein transcription factor stimulates gene transcription)
Light, through its various components, has direct and visible effects on our bodies. An example?
It stimulates the production of melanin, which contributes to tanning.
Other effects are not visible but are important: sunlight stimulates the production of Vitamin D.
At the cellular level, visible red and near-infrared light energy stimulates mitochondria to generate more energy converted to ATP for cellular use.
Mitochondria perform the function of producing cellular energy called 'ATP'.
This production process involves the respiratory chain.
A mitochondrial enzyme called cytochrome oxidase accepts the photon energy.
In addition, the process leads to cell repair and healing.
The process also unblocks the chain that has been blocked by nitric oxide (NO).
Nitric oxide is then released back into the system.
Nitric oxide helps to dilate blood vessels and improve blood circulation.
Parameters: The correct wavelength for the target cells, the chromophores (620- 810 nm), must be used.
If the wavelength is not correct, optimal absorption will not occur, without absorption there can be no reaction.
The absorption of light energy by enzine results in an increase in enzyme activity, cytochrome oxidase and oxygen consumption.